Vitamin B 12 also known as cobalamin, is an important water-soluble vitamin.
It is one of the other B vitamins. It is a significant micronutrient which contributes towards the body’s functioning.
Vitamin B12 functions in Human Body:
- It’s an essential vitamin for the cells.
- It’s important for keeping your nerves, blood cells, and DNA healthy.
- It is required to improve & maintain energy, mood & memory.
- It’s necessary for The proper functioning of your nervous system.
Usually, Animal products naturally contain this vitamin.
But that doesn’t mean that being a non vegetarian you can not consume it.
More than How much you eat, instead how your body absorbs vitamin B12 is essential. People who are non-vegetarian also have Vitamin B12 deficiency. Not the quantity but quality matters more. It’s not how more you consume Vitamin B12, instead how your body digests and absorbs it is important. Therefore, for good absorption and digestion of Vitamin B12, it’s important to have a healthy gut and digestive system.
Now once you know what is Vitamin B12, and what it does to your body, next question arises:
How much Vitamin B12 do you need on Daily Basis?
This answer may vary from person to person, because everyone’s body and age requirements are bio-individual and not at all same.
| Age/ Life Stages | Recommended Amounts |
| Infant-Children (till 10 years) | 0.5-1.5 mcg. |
| Teenagers | 1.8-2.4 mcg. |
| Adult | 2.4 mcg. |
| Pregnant women | 2.6 mcg. |
| Nursing mothers | 2.8 mcg. |
Bonus : Your liver can store vitamin B12 for future use.
Causes of B12 deficiency.
- If your diet is deficient in source of Vitamin B12.
- If you aren’t able to digest and absorb the ingested sources of vitamin B12.
- Unhealthy gut and poor digestive health can hinder the adequate absorption of Vitamin B12 in your body.
- High levels of stress and lack of sleep also contributes in disruption of proper functioning of body, which in turn effects its absorption.
- Unhealthy & poor lifestyle is another cause.
- Bad eating habits.
- Imbalanced diet.
- Eating lots of processed food which are loaded with chemicals and preservatives also effects.
Unfortunately, symptoms of a vitamin B12 deficiency can take years to show up, and diagnosing, and it can be complex.
Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency.
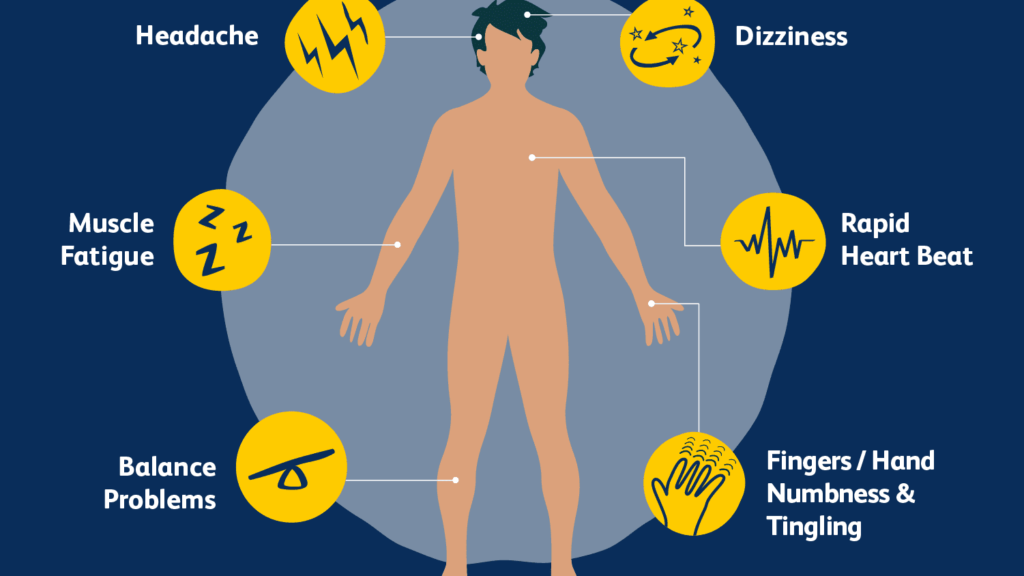
- Pale skin.
- Headache.
- Muscle pain and weakness.
- Fatigue & lack of energy.
- Depression.
- Mood swings.
- Imbalance & change of mobility.
- Breathlessness or dizziness.
- Vision problem.
- Numb and tingling in fingers.
- Lack of concentration & poor memory.
Facts about Vitamin B12!
- All seeds contain B 12 since it’s necessary for their survival.
- B-12 is made by bacteria in soil and absorbed by plants. Hence, all plants at a certain growth stage have it.
- In fact, animals like cows and sheep have B 12 because they eat plants.
- There are numerous plant-based sources of B 12 and B complex vitamins.
- There is a research that suggests if you have a clean and healthy gut, your body itself can produce enough B 12.
- We can’t get VitaminB12 through plant sources directly, but we can produce it within our gut or stomach, if we have good bacterial flora or Balance in our gut.
- Germination is one way of improving Vitamin B12. Sprouting of grains, pulses and legumes increases its content.
- Absorption of vitaminB12 is the major problem rather than their availability in diet.
- Lack of enzymes, good bacteria and wrong stomach acids makes it difficult to synthesize the vitamin.
- We have many good bacteria in our gut, for example: lactobacillus which can help us produce or make enough vitamin B-12 that we need.
- We Need a variety of good bacteria to create a good environment for VitB12 production.
- Fermentation of grains specially millets is the best way of increasing Vitb12 in diet and increasing its absorption. Fermenting millets like ragi, foxtail millet, little millet, barnyard millet can help. Examples of fermented recipes are khooz, ambali, kanji, kavass.
- Other Vegetarian & Vegan sources of Vitamin B12: Dairy products( curd, buttermilk), nutritional yeast, Nori Seaweed, some mushrooms, fortified food, tempeh.
Vegetarian sources of Vitamin B12 with Nutritional Estimations:

- Homemade Paneer. One Cup 250g : 1.1 mcg Vitamin B12
- Fermented Millets ( cook millets, leave overnight ) Ambli. One Cup Fermented Millets : 0.7 mcg ( Greater Absorption )
- Probiotics. Supports Healthy gut to improve Absorption.
- Germinated food ( sprouts )
- Nutritional yeast. One Tbsp Nutritional Yeast : 4 mcg
- Nori seaweed. One sheet (2.5g) : more than 2.4 mcg ( 100% RDI). Spirulina, Chlorella, Green & Purple Laver, Dulse, Wakame
- Shiitake mushrooms. 50g Sun-dried : 100% RDI
- Fermented vegetable & Tea ( Kombucha) 100g fermented veggies : 0.8mcg
- Green juice ( wheat grass, barley grass) One serving : 0.4-0.6 mcg ( low absorption).
ENDNOTE
Until now, you might have heard of Vitamin B12 deficiency, how to prevent it? or What are the richest food sources of it? But more than half of you did not knew that digestion and absorption of Vitamin B12 is much more important than it’s availability. Be self aware, and try to know as much as you can about what you eat and how can you improvise it for a better and healthy lifestyle.
